Concepts
Jobset
A JobSet creates one or more Jobs. It allows you to create sets of jobs of different or identical templates, and control their lifecycle together.
Conceptual Diagram
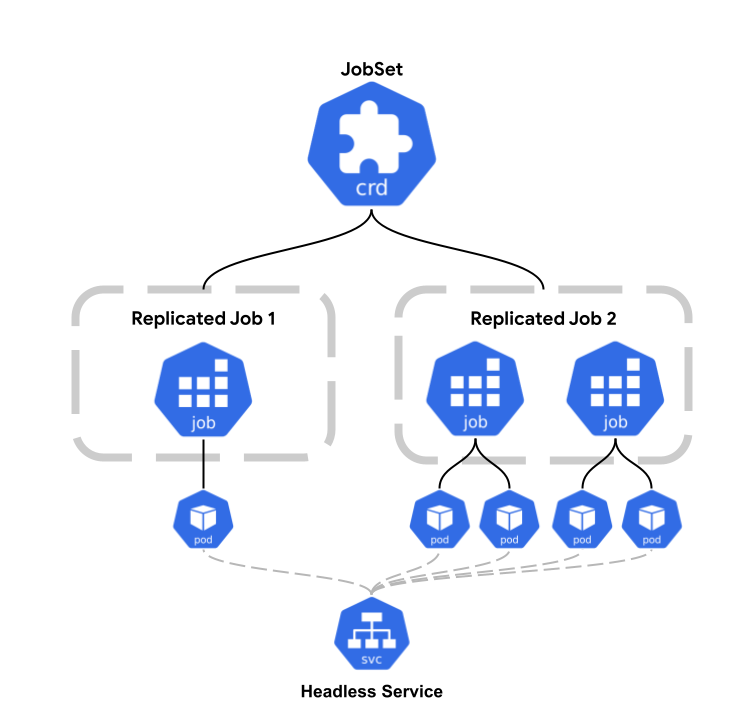
Running an Example JobSet
Here is an example JobSet. It runs a distributed PyTorch training workload.
apiVersion: jobset.x-k8s.io/v1alpha2
kind: JobSet
metadata:
name: pytorch
spec:
replicatedJobs:
- name: workers
template:
spec:
parallelism: 4
completions: 4
backoffLimit: 0
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: pytorch
image: gcr.io/k8s-staging-jobset/pytorch-resnet:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 3389
env:
- name: MASTER_ADDR
value: "pytorch-workers-0-0.pytorch"
- name: MASTER_PORT
value: "3389"
command:
- bash
- -xc
- |
torchrun --nproc_per_node=1 --master_addr=$MASTER_ADDR --master_port=$MASTER_PORT resnet.py --backend=gloo
To list all the jobs that belong to a JobSet, you can use a command like this:
kubectl get jobs --selector=jobset.sigs.k8s.io/jobset-name=pytorch
The output is similar to
NAME COMPLETIONS DURATION AGE
pytorch-workers-0 0/4 6m12s 6m12s
To list all the pods that belong to a JobSet, you can use a command like this:
kubectl get pods --selector=jobset.sigs.k8s.io/jobset-name=pytorch
The output is similar to
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pytorch-workers-0-0-tcngx 1/1 Running 0 13m
pytorch-workers-0-1-sbhxs 1/1 Running 0 13m
pytorch-workers-0-2-5m6d6 1/1 Running 0 13m
pytorch-workers-0-3-mn8c8 1/1 Running 0 13m
JobSet defaults for Jobs and Pods
- Job
completionModeis defaulted toIndexed - Pod
restartPolicyis defaulted toOnFailure
JobSet labels
JobSet labels will have jobset.x-k8s.io/ prefix. JobSet sets the following labels on both the jobs and pods:
jobset.sigs.k8s.io/jobset-name:.metadata.namejobset.sigs.k8s.io/replicatedjob-name:.spec.replicatedJobs[*].namejobset.sigs.k8s.io/replicatedjob-replicas:.spec.replicatedJobs[*].replicasjobset.sigs.k8s.io/job-index: ordinal index of a job within aspec.replicatedJobs[*]
ReplicatedJob
The list .spec.replicatedJobs allows the user to define groups of Jobs of different templates.
Each entry of .spec.replicatedJobs defines a Job template in spec.replicatedJobs[*].template,
and the number replicas that should be created in spec.replicatedJobs[*].replicas. When
unset, it is defaulted to 1.
Each Job in each spec.replicatedJobs gets a different job-index in the range 0 to .spec.replicatedJob[*].replicas-1.
The Job name will have the following format: <jobSetName>-<replicatedJobName>-<jobIndex>.
DNS hostnames for Pods
By default, JobSet configures DNS for Pods by creating a headless service for each spec.replicatedJobs.
The headless service name, which determines the subdomain, is .metadata.name-.spec.replicatedJobs[*].name
To list all the headless services that belong to a JobSet, you can use a command like this:
kubectl get services --selector=jobset.sigs.k8s.io/jobset-name=pytorch
The output is similar to
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
pytorch-workers ClusterIP None <none> <none> 25m
Exclusive Job to topology placement
The JobSet annotation alpha.jobset.sigs.k8s.io/exclusive-topology defines 1:1 job to topology placement.
For example, consider the case where the nodes are assigned a rack label. To optimize for network
performance, we want to assign each job exclusively to one rack. This can be done as follows:
apiVersion: jobset.x-k8s.io/v1alpha2
kind: JobSet
metadata:
name: pytorch
annotations:
alpha.jobset.sigs.k8s.io/exclusive-topology: rack
spec:
replicatedJobs:
- name: workers
template:
spec:
...
JobSet termination
A JobSet is marked as successful when ALL the Jobs it created completes successfully.
A JobSet failure is counted when ANY of its child Jobs fail. spec.failurePolicy.maxRestarts defines how many times
to automatically restart the JobSet. A restart is done by recreating all child jobs.
A JobSet is terminally failed when the number of failures reaches spec.failurePolicy.maxRestarts